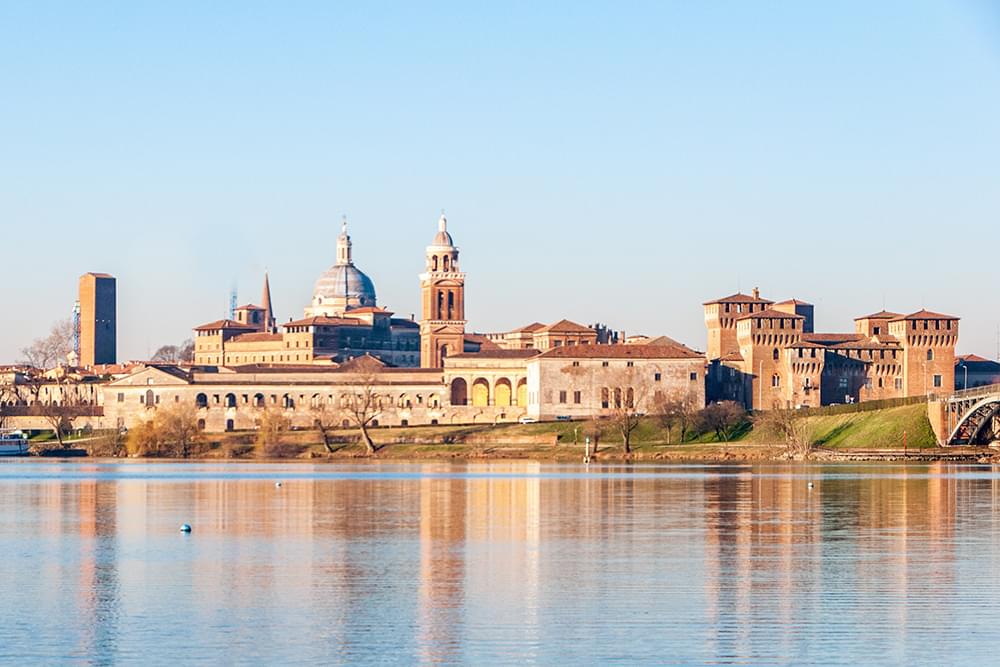
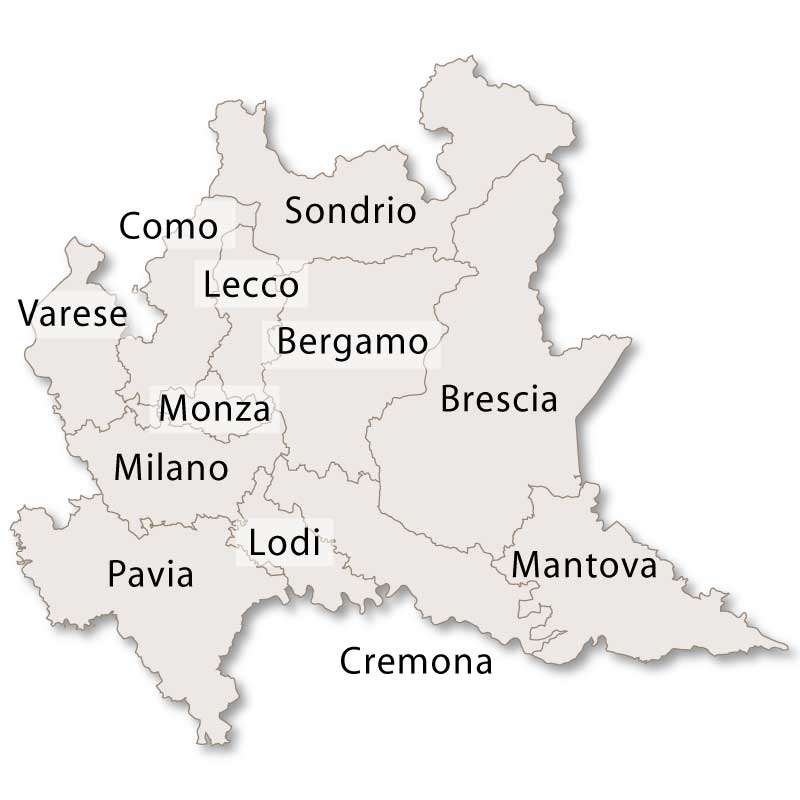
The province of Mantova is on the far eastern border of the region of Lombardy and covers an area of 2,339 sq.km. It is bordered to the north east and east by the region of Veneto, to the south by the region of Emilia- Romagna, to the west by the province of Cremona and to the north west by the region of Brescia.It's southern border runs along the bank of the River Po and is subject to flooding.

It is a flat and fertile province with an irrigation system that was designed in part by Leonardo da Vinci. There are several protected areas and nature reserves throughout the province including the Parco regionale del Mincio, the Parco dell'Oglio Sud and the Riserva naturale Bosco Fontana.
The capital city is Mantova with the second city being Castiglione delle Stiviere.
Other main towns in the province of Mantova are:
Located in the northern É«ÖĐÉ« region of Lombardy, Mantova (Mantua) Province is a land steeped in history, culture, and natural beauty. Known for its stunning Renaissance architecture, picturesque landscapes, and cultural legacy, Mantova is one of Italy’s most charming yet underappreciated provinces. The capital city of Mantua is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, primarily due to its remarkable artistic and architectural contributions during the Renaissance, particularly under the powerful Gonzaga family. Beyond its historical importance, the province is also known for its rich agricultural tradition and beautiful natural reserves.
Mantova Province lies in the southeastern part of Lombardy, bordered by the provinces of Verona, Modena, Cremona, and Reggio Emilia. The province’s geography is largely flat and fertile, making it ideal for agriculture, which has historically been the backbone of the local economy. It is surrounded by three artificial lakes: Lago Superiore, Lago di Mezzo, and Lago Inferiore, all fed by the Mincio River. These lakes, along with the lush countryside, contribute to Mantova’s scenic beauty.
Mantova enjoys a temperate climate, with hot summers and cold winters. The presence of the lakes creates a high level of humidity, leading to misty mornings during the colder months. This climate, along with the fertile plains, has made the region one of Italy’s agricultural powerhouses, particularly known for its rice fields and production of vegetables, fruits, and dairy products.
The history of Mantova Province is deeply intertwined with the city of Mantua, which has long been a center of power, culture, and learning. Originally settled by the Etruscans and later the Romans, Mantua developed into a significant urban center in northern Italy. However, it was during the Renaissance that Mantua rose to prominence, primarily under the rule of the Gonzaga family.
The 'Gonzaga dynasty' transformed Mantua into a cultural and artistic hub, attracting renowned artists, architects, and scholars from across Europe. Their patronage of the arts led to the construction of magnificent palaces, churches, and public spaces, many of which remain standing today. In 1328, Ludovico Gonzaga became the ruler of Mantua, and the family’s reign continued for nearly four centuries. During this time, Mantua became a shining example of Renaissance humanism and innovation, fostering the work of artists such as 'Andrea Mantegna' and 'Giulio Romano'.
In 1708, the Gonzaga rule came to an end, and Mantua fell under the control of the Austrian Habsburgs. It became part of the Kingdom of Italy in the 19th century, and while the Renaissance glory had faded, Mantua remained an important cultural center.
Mantova Province is often referred to as a living museum of the Renaissance. The historic center of Mantua, along with nearby Sabbioneta, was designated a 'UNESCO World Heritage Site' in 2008, highlighting the province’s contribution to the development of Renaissance urban planning and architecture.
At the heart of Mantua is the 'Palazzo Ducale', the grand palace complex that was the seat of the Gonzaga family. Covering an area of over 34,000 square meters, it is one of the largest palace complexes in Europe. The palace includes over 500 rooms, featuring frescoes, tapestries, and artworks from some of the Renaissance’s greatest artists. A highlight of the complex is the 'Camera degli Sposi (Bridal Chamber)', painted by Andrea Mantegna, which is celebrated for its pioneering use of perspective and trompe-l'œil.
Another architectural masterpiece is the 'Palazzo Te', designed by Giulio Romano in the 16th century. The palace was built as a leisure residence for the Gonzagas and features bold Mannerist architecture and stunning frescoes. The most famous room in the palace is the 'Sala dei Giganti (Hall of the Giants)', where Romano’s frescoes depict the fall of the giants in vivid and dynamic detail.
In addition to its palaces, Mantua is home to several notable churches, such as the 'Basilica di Sant'Andrea', designed by 'Leon Battista Alberti'. The basilica, completed in 1472, is one of the finest examples of Renaissance architecture in Italy and is believed to house a relic of the Holy Blood, making it an important religious site.
While Mantua itself is a treasure trove of Renaissance art and architecture, the nearby town of 'Sabbioneta' offers a fascinating glimpse into Renaissance urban planning. Founded by Vespasiano Gonzaga in the 16th century, Sabbioneta was designed as an ideal city based on humanist principles. It is often called a "Renaissance utopia" because of its perfectly planned streets, squares, and buildings. Some notable landmarks in Sabbioneta include the 'Palazzo Ducale', the 'Teatro all'Antica' (one of the earliest indoor theaters in the world), and the 'Galleria degli Antichi'.
Mantova Province is also blessed with natural beauty, especially its network of lakes and rivers. The 'Mincio River' runs through the province, feeding Mantua’s famous lakes and providing a vital lifeline for the region’s agriculture and biodiversity.
The 'Parco del Mincio' is a regional park that protects the wetlands and river ecosystems surrounding Mantua. The park is a haven for birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts, as it is home to a wide variety of bird species, including herons, kingfishers, and swans. The park’s peaceful trails are perfect for hiking and cycling, offering visitors a chance to immerse themselves in the serene natural landscape.
Additionally, 'Bosco Fontana', a historic forest located near the town of Marmirolo, is one of the few remaining examples of the ancient Po Valley forest. It is a natural reserve that provides a unique ecosystem for various plant and animal species, making it a popular destination for eco-tourism and educational visits.
Mantova Province is renowned for its rich culinary tradition, deeply rooted in the region’s agricultural bounty. The province’s fertile plains produce an abundance of high-quality ingredients, which form the basis of its local dishes.
One of Mantova’s most famous dishes is 'tortelli di zucca', a type of stuffed pasta filled with sweet pumpkin, amaretti biscuits, and Parmesan cheese. The dish is typically served with melted butter and sage, creating a delicious balance of sweet and savory flavors.
'Risotto alla pilota', made with locally grown rice and pork sausage, is another staple of Mantuan cuisine, reflecting the region’s long history of rice cultivation. The province is also known for its 'salami', particularly 'salame mantovano', and cured meats, which are often served with 'mostarda di frutta', a tangy fruit condiment.
For dessert, Mantua offers the unique 'sbrisolona', a crunchy almond cake that is typically enjoyed with a glass of dessert wine. Additionally, the province is known for producing high-quality 'Grana Padano' cheese, one of Italy’s most famous cheeses, which is widely used in both cooking and as a standalone delicacy.
Mantova Province is home to a vibrant array of cultural events and festivals throughout the year. One of the most significant is the 'Festivaletteratura', an annual literary festival that attracts authors, poets, and readers from around the world. Held every September in Mantua, the festival celebrates literature with readings, discussions, and workshops, bringing the city’s Renaissance past into conversation with contemporary culture.
Other notable events include the 'Palio di San Benedetto Po', a medieval festival that takes place in the town of San Benedetto Po, and various food festivals dedicated to local products such as pumpkin, rice, and Grana Padano cheese.
While agriculture remains an essential part of the local economy, Mantova has diversified in recent decades. The province has a growing industrial sector, particularly in the fields of machinery, food production, and chemicals. The proximity to larger industrial centers like Milan and Verona provides Mantova with opportunities for economic growth while retaining its unique cultural and rural identity.
Tourism also plays a crucial role in Mantova’s economy, with visitors drawn to its artistic heritage, scenic landscapes, and culinary offerings. The designation of Mantua as a UNESCO World Heritage Site and its inclusion in the 'European Capitals of Culture' in 2016 have helped raise the province’s profile as a cultural destination.
Mantova Province is a region that offers a perfect blend of history, culture, and natural beauty. Whether you are drawn to its Renaissance art and architecture, its peaceful parks and lakes, or its rich culinary traditions, Mantova provides an enriching experience that captures the essence of Italy’s cultural and historical heritage. From the grandeur of Palazzo Ducale to the tranquil landscapes of the Mincio River, Mantova is a province where the past and present harmoniously coexist, inviting travelers to explore its timeless beauty and hidden gems.
| Ěý | High | Low | Sun | Rain |
| Jan | 11 | 2 | 3 | 55 |
| Feb | 12 | 3 | 4 | 53 |
| Mar | 14 | 4 | 5 | 63 |
| Apr | 18 | 7 | 6 | 55 |
| May | 22 | 11 | 8 | 35 |
| Jun | 26 | 15 | 9 | 44 |
| Jul | 29 | 17 | 10 | 34 |
| Aug | 29 | 17 | 9 | 54 |
| Sep | 25 | 14 | 7 | 61 |
| Oct | 21 | 11 | 6 | 74 |
| Nov | 16 | 8 | 4 | 71 |
| Dec | 12 | 3 | 3 | 77 |
| Table Key: High - Average monthly high temperatures Low - Average monthly low temperatures Sun - Average hours of sunshine per day Rain - Average monthly rainfall in mm |
||||